The challenge
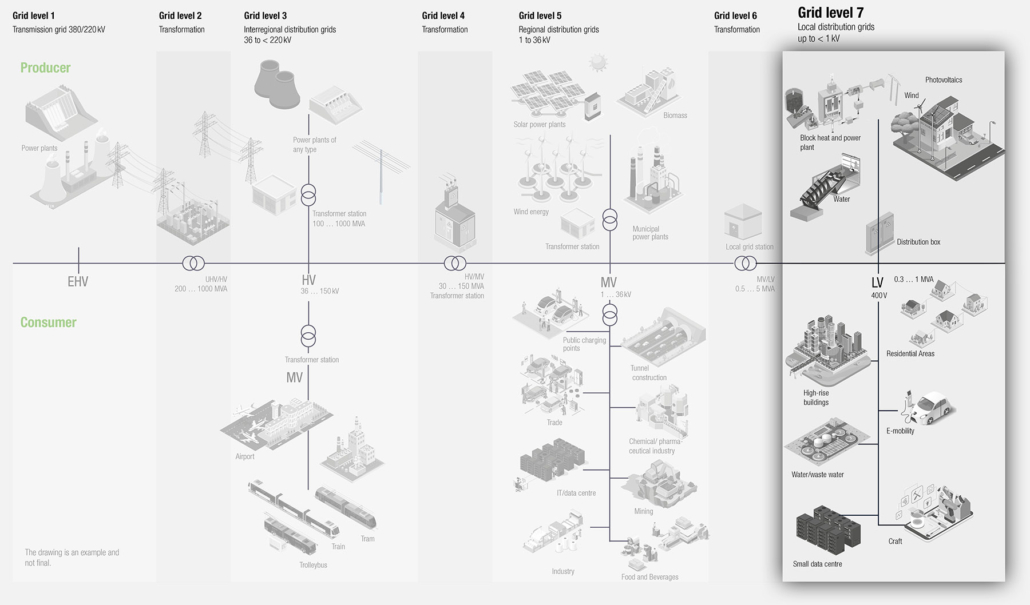
One of the great challenges is that the formerly centralised electrical energy world has developed into a highly dynamic as well as very complex decentralised system. In this process, it must be possible to systemically process new but relevant information in a targeted handling of data.
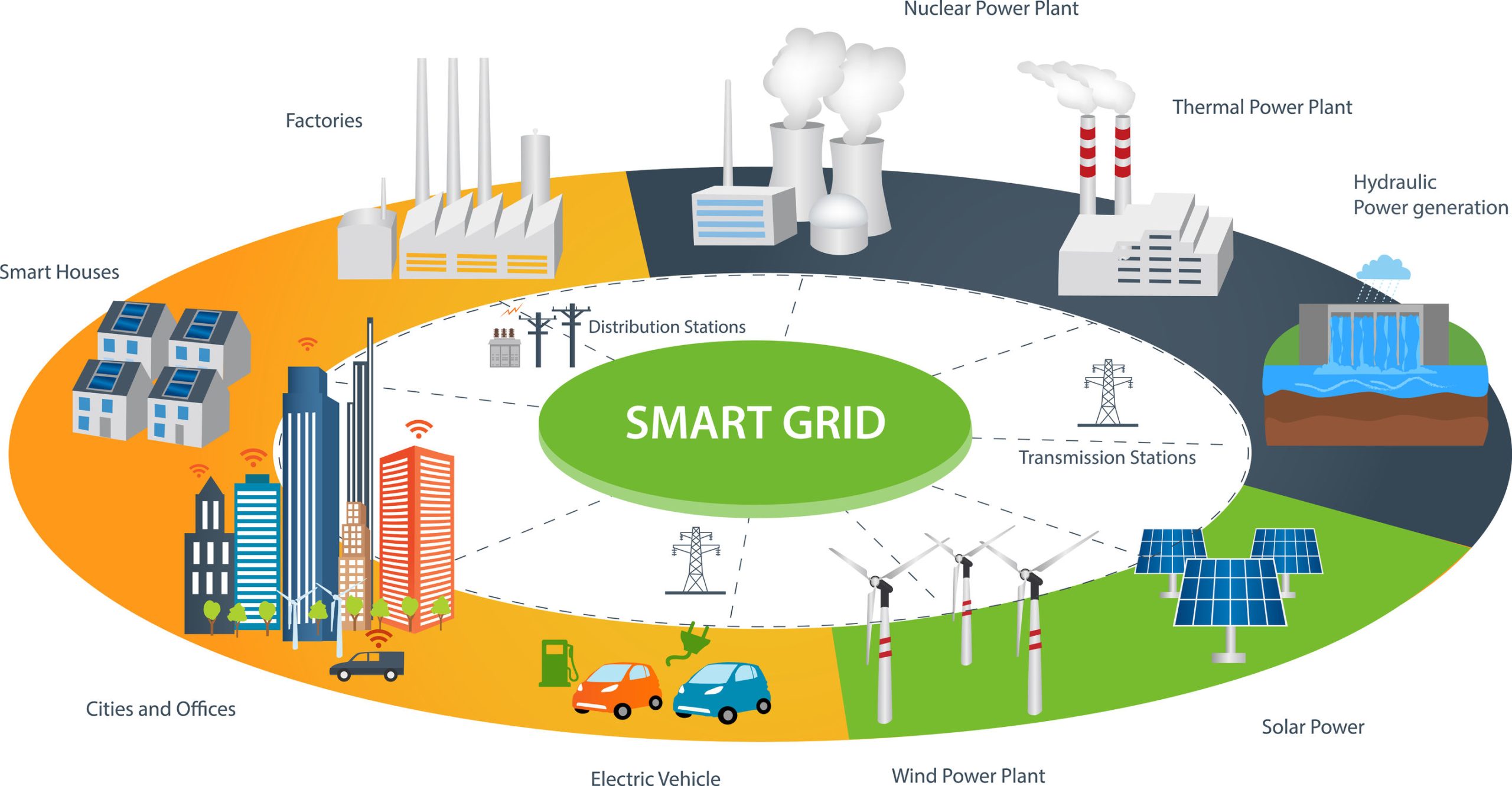
Definition Smart Grid
A smart grid is understood to be an electrical system that intelligently ensures the exchange of electrical energy from different sources with consumers of different demand characteristics by incorporating measurement and mostly digital information and communication technologies. Such a system should take into account the needs of all market players and society. The use and operation of the system can thus be optimised and made more efficient, and the costs and environmental impact can be minimised.
the environmental impact can be minimised and the quality and security of supply can be guaranteed to a sufficiently high degree.
Source: Bundesamt für Energie BFE
Effects of a smart grid on measurement technology
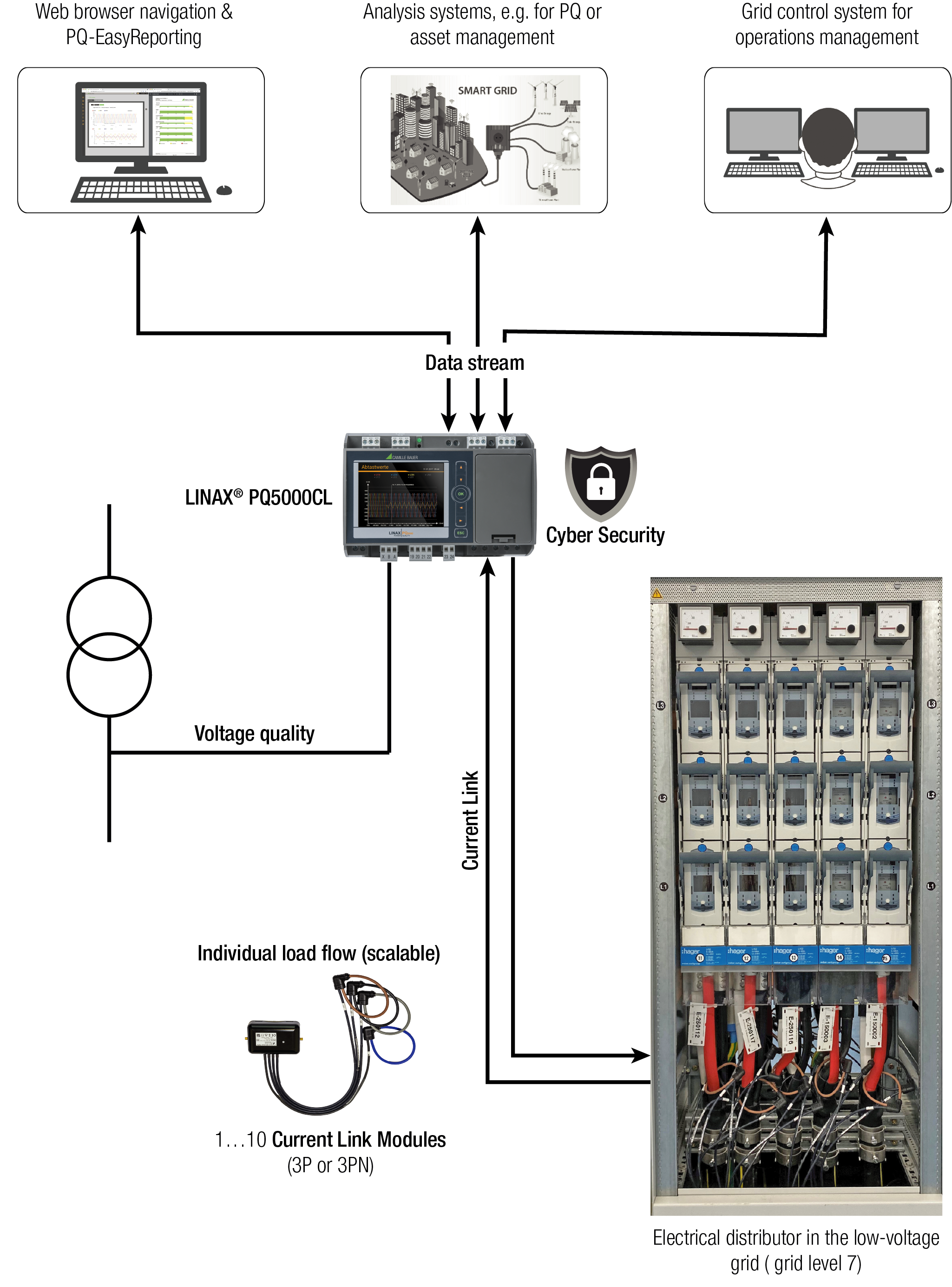
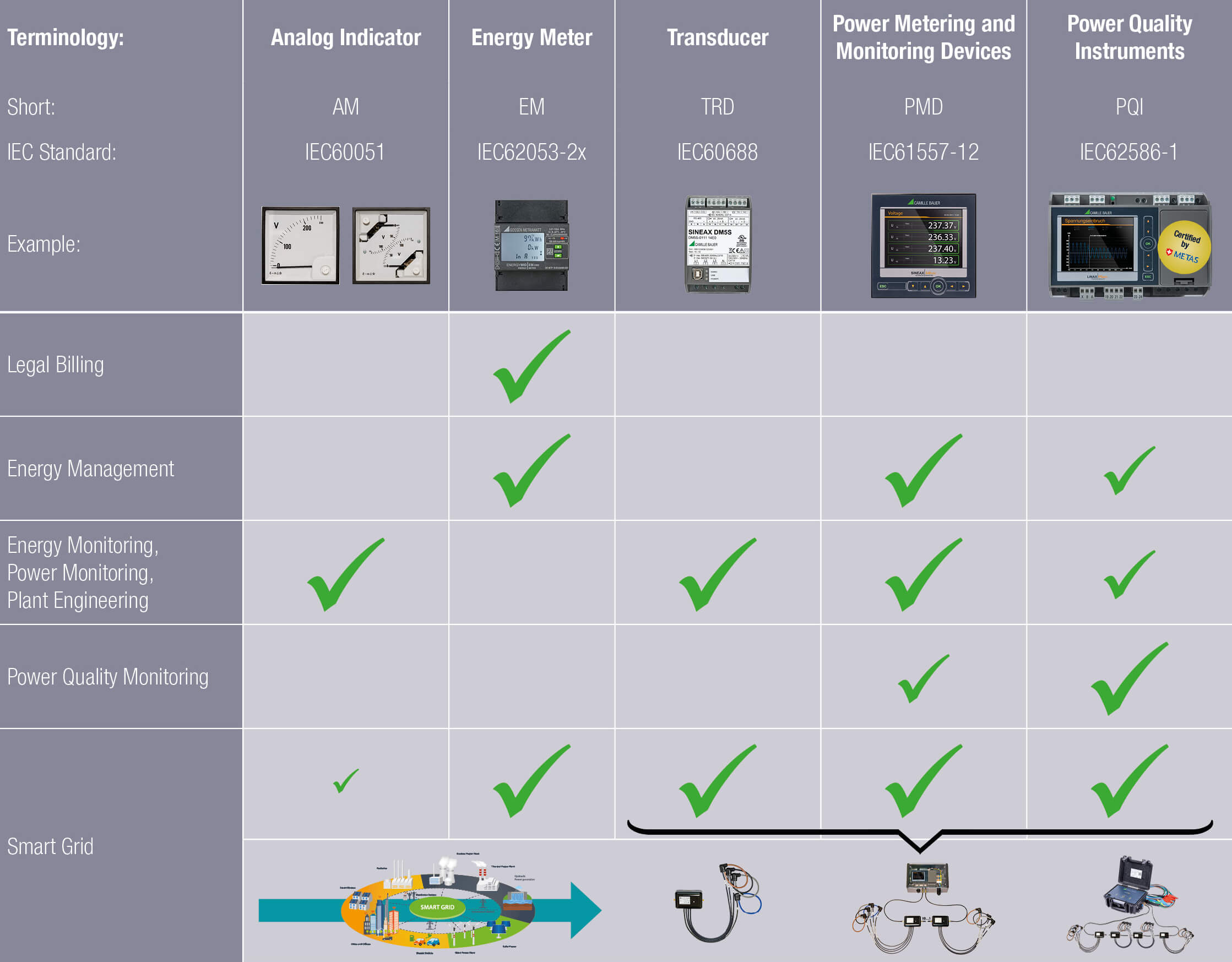
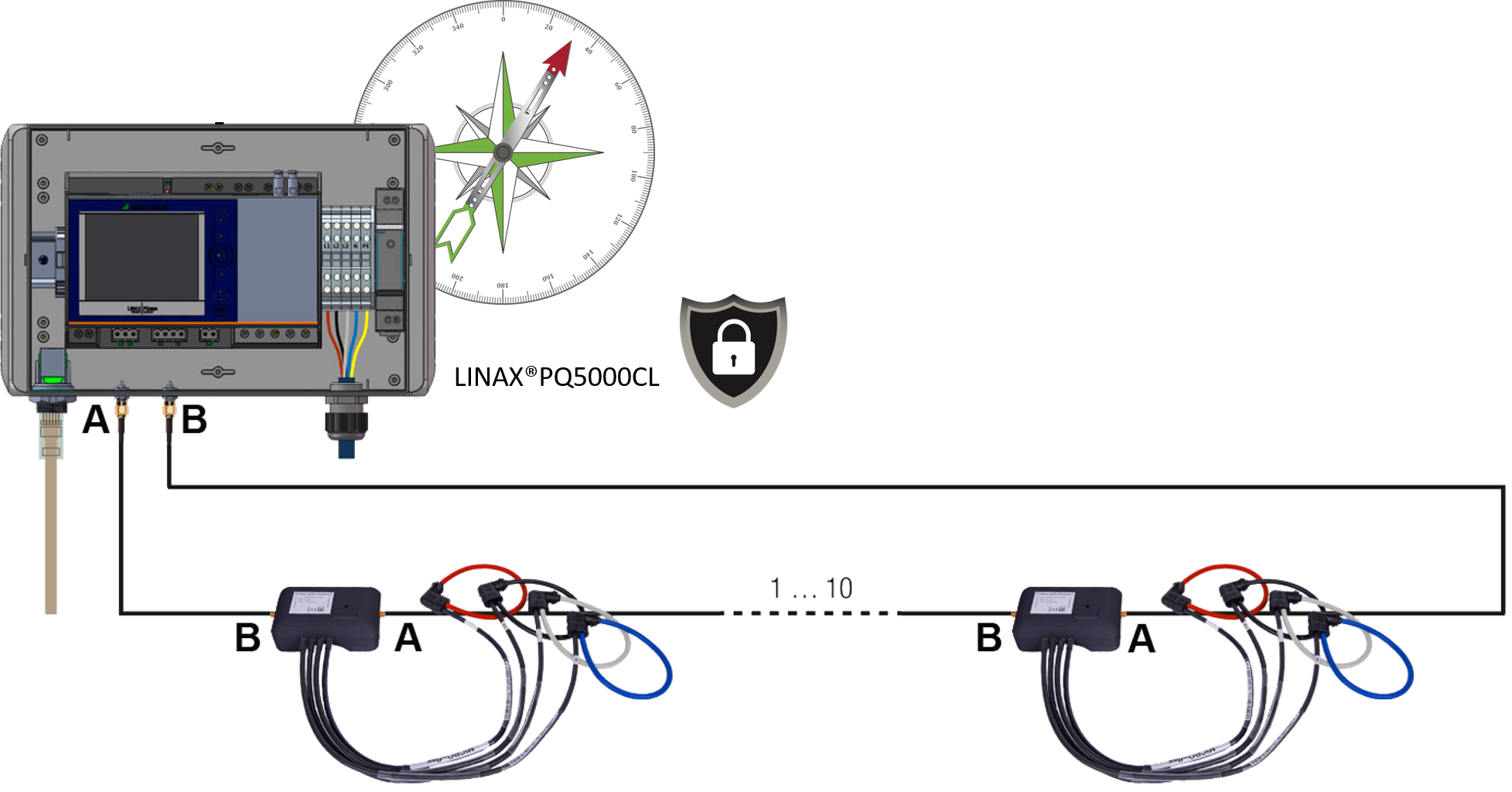
Basically, the common measurement data of voltage, current and frequency as well as their derived quantities are still required. However, and here comes the possible challenge for the smart grid application: The measurement data will be combined with new customer needs and put into relation (e.g. scalability, real-time, connection to existing control systems, integration into new platform solutions, connectivity, distinct technical consulting needs, cyber security, additional costs, etc.). Thus, the conventional IEC groupings of electrical measuring devices will possibly change and overlap even more in order to enable transparency in the smart grid.
In addition, it certainly makes sense to continue to use analogue indicators (electromechanical) redundantly for essential functions. These can withstand any failure and/or attack of a data communication. This is also clear from the matrix shown below.